How to determine the best crown and bridge material for your patient’s implant case?
- By, Admin
- 20 Dec, 2023
Throughout the last fifty years, materials used for dental implants have been extensively researched, and an understanding of how the physical and chemical properties affect the clinical outcome of the treatment has considerably improved.
Dental
crowns and bridges are two forms of dentistry used to repair damaged
teeth or replace teeth lost secondary to caries, trauma, periodontal
disease, etc. For patients, regaining function and improving aesthetics
are often important criteria for dental implant treatment. Throughout
the last fifty years, materials used for dental implants have
been extensively researched, and an understanding of how the physical
and chemical properties affect clinical outcomes of treatment has
considerably improved. These properties include the surface composition and microstructure
of dental implants. Ideally, implant materials should be biocompatible
and resistant to corrosion and fracture. Implants can be made from
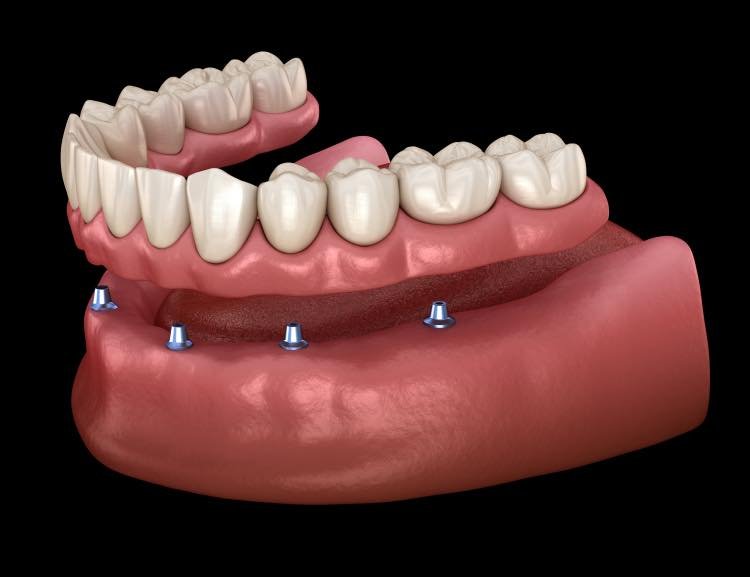
titanium or zirconia (ceramic). At DDS Lab, the material we
recommend for crown and abutment restorations will depend on several
factors, including which tooth is being replaced, the presence or
absence of parafunctional habits, and metal allergies. Before choosing
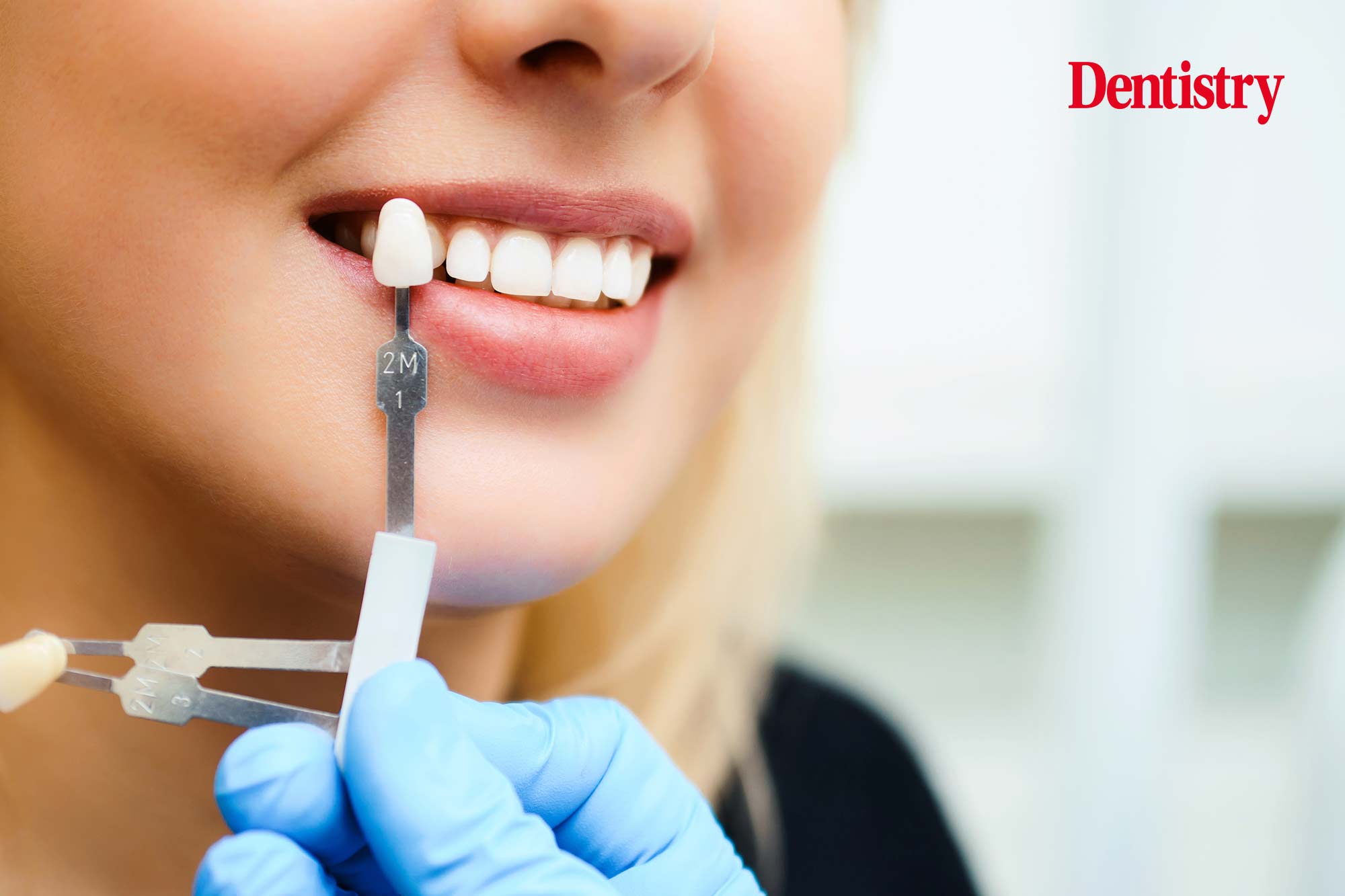
the material for crowns or fixed prostheses, it is essential to discuss
the benefits and limitations of each option. Restorative dentists who do not place
implants need to know the following points regarding the implants that
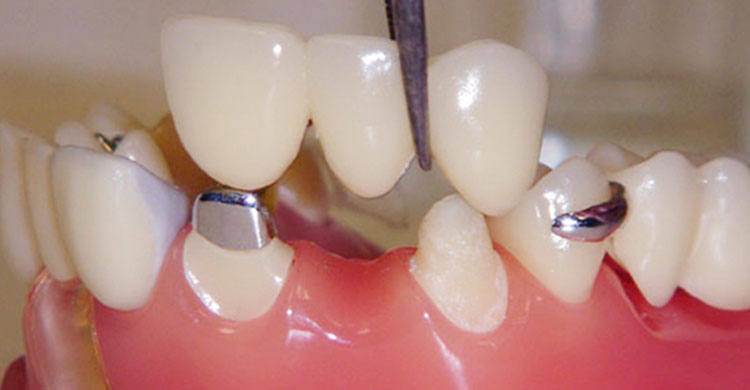
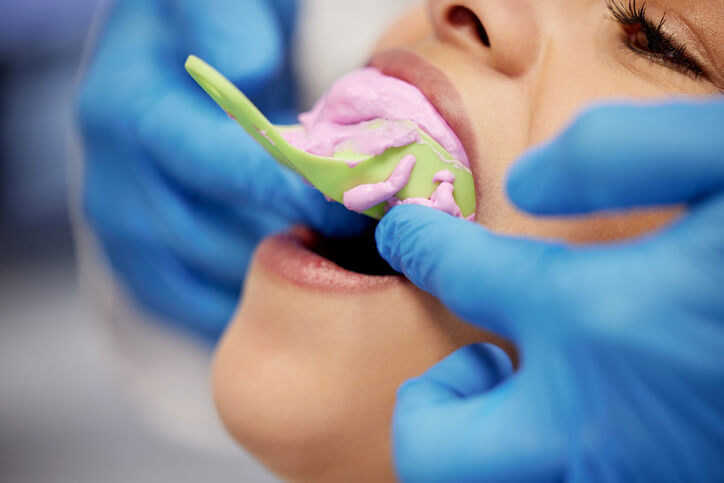
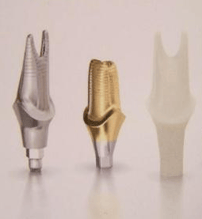
they will be restoring: Abutments are implant restorative components screwed directly into dental implants. Image: Abutments made from titanium, titanium with gold titanium nitride, and zirconia (left to right). They include: They may be machined from many materials, including titanium,
zirconia, base metal, PMMA, high-performance polymers (HPP), and
composite resins. Definitive abutments are typically manufactured from
titanium, zirconia, or base metals. They may be used for cement- and
screw-retained restorations. Stock abutments may be fabricated with materials similar to custom
abutments. They are available in multiple shapes, angles, and margin
collar heights. They are generally less expensive than custom abutments. As the name suggests, porcelain fused to metal (PFM) crowns combine
porcelain and metal. The porcelain overlay is color-matched to the
patient’s natural teeth. Sometimes, the dark metal margin could show at
the gingival margin, especially with gingival recession or high smile
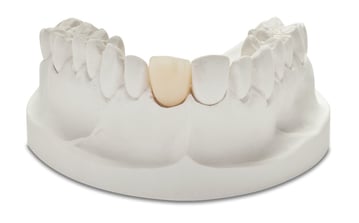
lines. Dentists may recommend PFM restorations for patients who desire strength and a natural appearance. Zirconia restorations are ceramic-type restorations; they are not metal. They may fracture more easily than PFM crowns. Zirconia,
a metal in the periodic table of elements, is found worldwide. Everyday
household items such as dinnerware, pipes, and electrical fixtures are
made from zirconia. Because of its natural strength and durability, zirconia may be used
with excellent results for dental crowns. Zirconia crowns are best for
patients who need posterior crowns, which require greater strength for
masticating food and parafunctional habits. They are generally more
opaque than feldspathic porcelains or lithium disilicate restorations. The skilled technicians at DDS Lab have in-depth knowledge about
zirconia, titanium, and PFM materials used for restorations and are
always willing to discuss specific cases with you.

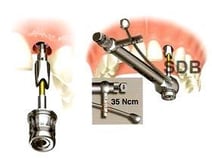
Abutment Types for Dental Implants
Custom Designed (CAD/CAM) Abutments and Crowns
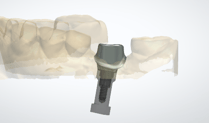
Image: Computer design of a titanium abutment for use with a cement-retained crown.|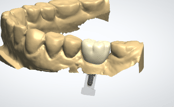
Image: A digitally designed zirconia crown on the CAD-designed titanium abutment above.
Image: CAD/CAM zirconia abutments.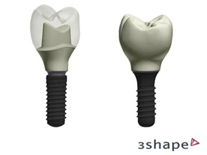
Image: Cement-retained zirconia crown and CAD/CAM zirconia abutment.
Stock Abutments

Image: Stock Abutments
Porcelain Fused-to-Metal (PFM) Dental Implant-Supported Restorations

Image: Custom or stock abutments may be used for cement-retained restorations such as PFM crowns.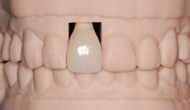
Image: PFM crown in place on die (digital workflow).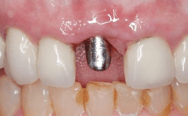
Image: Titanium abutment in place. This abutment replicated the plastic die in the above image.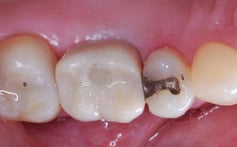
Image: PFM crowns can also be used for screw-retained crowns.
Benefits of PFM restorations
Limitations of PFM restorations
Zirconia Dental Implant-Supported Restorations
Benefits of Zirconia
Limitations of Zirconia
 English
English ភាសាខ្មែរ
ភាសាខ្មែរ